There are a variety of ways to consume your medical cannabis, including inhalation, ingestion, topical application, and sublingual application. Using a variety of consumption methods can help you treat your conditions from many angles, and some methods may be more effective than others. The beauty of cannabis as medicine is that it takes some experimentation to discover what works best for each individual. In that exploration one may find relief in ways they are not expecting. It is important to know what your options are when it comes to methods of consumption.
Inhalation– Smoking & Vaping

Looking at the terpene profile information on your cannabis labels can be very helpful in teaching you more about your medicine. It can teach you which terpenes can be useful for your specific condition. For example, strains high in the terpene beta-Myrcene tend to be more sedative, analgesic, and accentuate the effects of THC by acting as a vehicle to break through the Blood Brain Barrier. Here we have featured Beautiful Nightmare, a mild Indica (night time sedative and relaxing) strain.

Inhaling vaporized cannabis can be a healthier option for your lungs and can also be more discreet if the processed product has been refined to remove terpenes and other plant matter that attribute to taste and smell that is associated with cannabis. It can also be more convenient for on-to-go relief.




Ingestion-Eating your Medicine



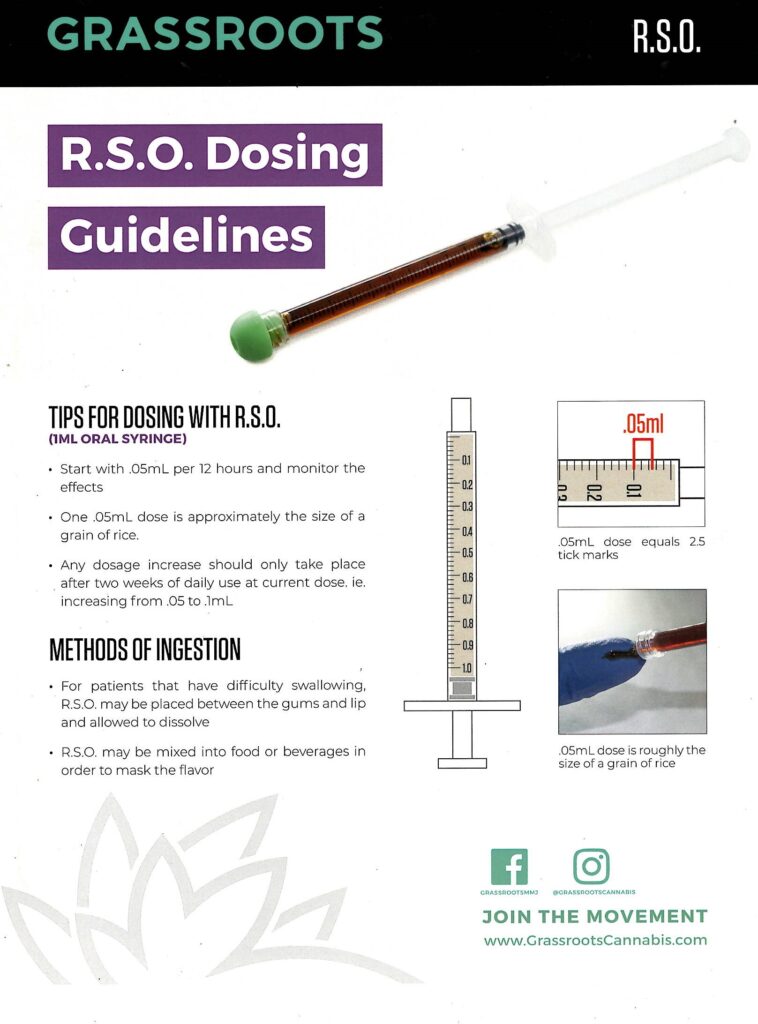



Topicals- Local Application than can be transdermal or topical




Sublingual/Tinctures- Drop your medicine underneath your tongue
Sublingual medical cannabis application works by absorption through the blood vessels that exist in the mouth underneath the tongue, cheeks, and gums. This helps to circulate your medication through your body, so you do not need to smoke in order to achieve medicated effects. This method does not take as long as ingestion, but it is not as quick of an onset as smoking. RSO can be administered sublingually as well. Tinctures can come in many forms, either infused with alcohol, coconut oil or MCT oil, or in grapeseed oil.